The middle of winter has long been a time of celebration around the world. Centuries before the arrival of the man called Jesus, early Europeans celebrated light and birth in the darkest days of winter. Many peoples rejoiced during the winter solstice, when the worst of the winter was behind them and they could look forward to longer days and extended hours of sunlight.
In Scandinavia, the Norse celebrated Yule from December 21, the winter solstice, through January. In recognition of the return of the sun, fathers and sons would bring home large logs, which they would set on fire. The people would feast until the log burned out, which could take as many as 12 days. The Norse believed that each spark from the fire represented a new pig or calf that would be born during the coming year.
The end of December was a perfect time for celebration in most areas of Europe. At that time of year, most cattle were slaughtered so they would not have to be fed during the winter. For many, it was the only time of year when they had a supply of fresh meat. In addition, most wine and beer made during the year was finally fermented and ready for drinking.
In Germany, people honored the pagan god Oden during the mid-winter holiday. Germans were terrified of Oden, as they believed he made nocturnal flights through the sky to observe his people, and then decide who would prosper or perish. Because of his presence, many people chose to stay inside.

Decorated trees date back to Germany in the Middle Ages, with German and other European settlers popularizing Christmas trees in America by the early 19th century.READ MORE: History of Christmas Trees
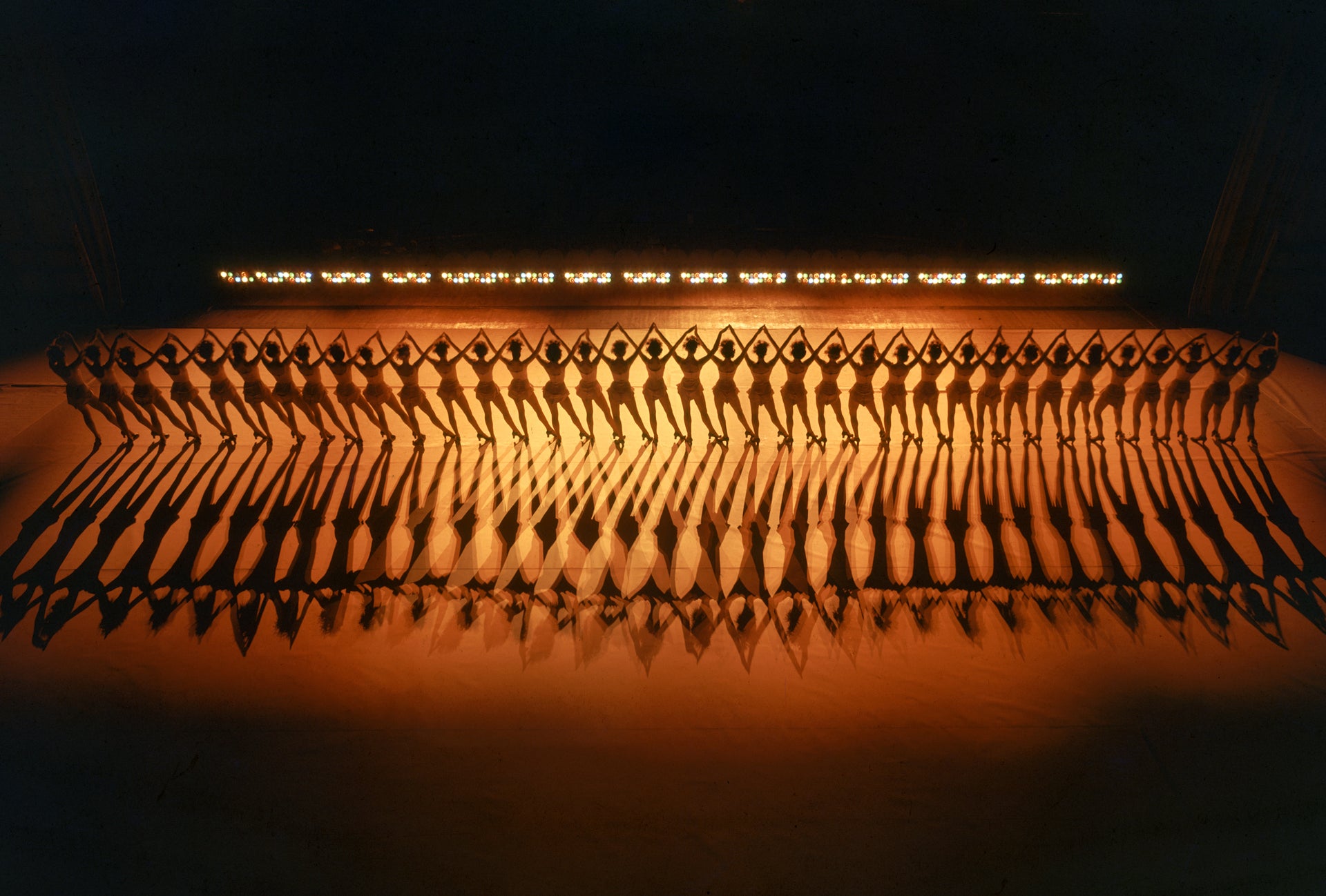
Since 1925, first known as the Missouri Rockets, this iconic dance troupe has been kicking up its heels, officially becoming the Radio City Music Hall Rockettes in 1934. They're best known for their annual Christmas show.
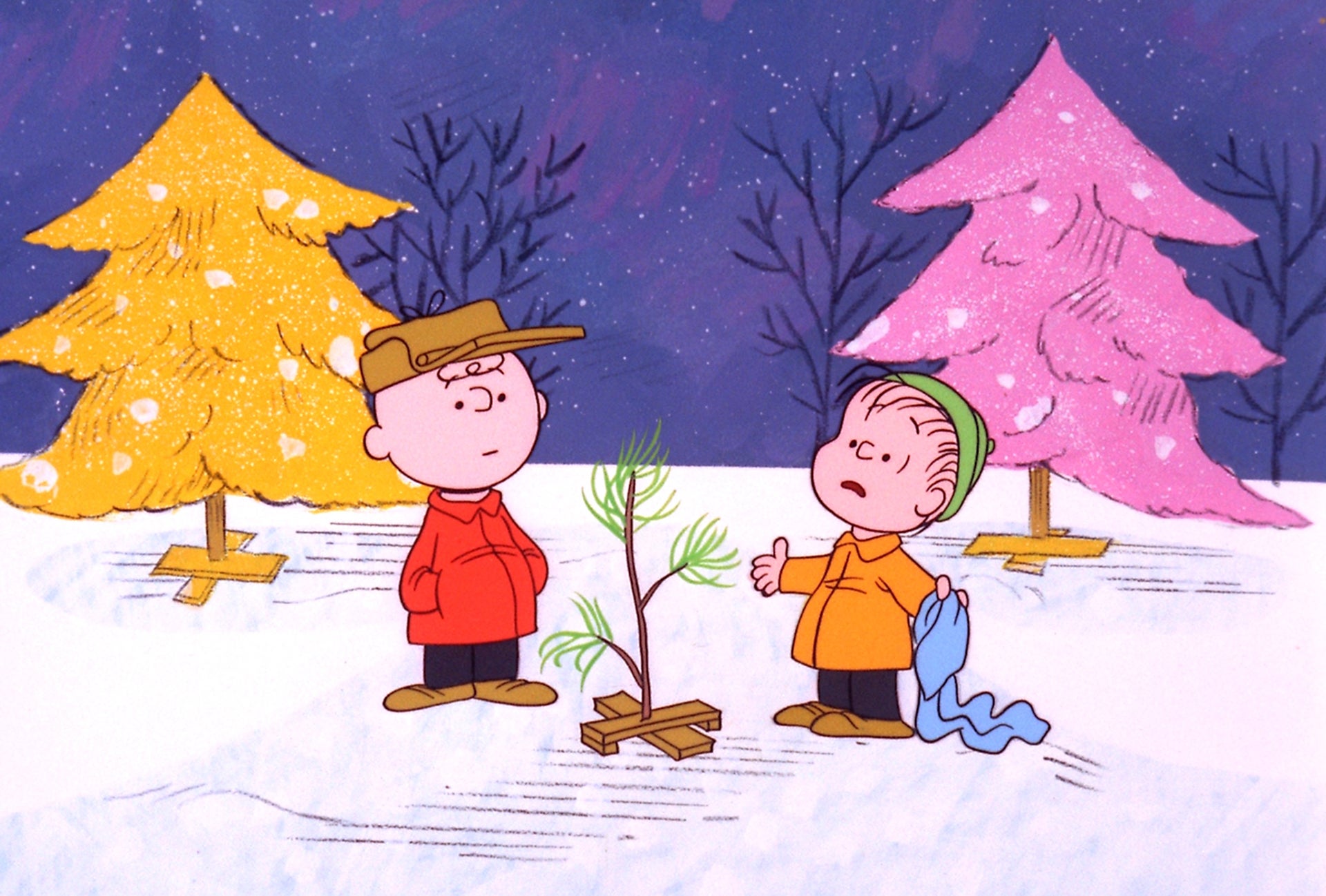

This beloved TV special inspired by Charles Schulz’s Peanuts comic strip was first rejected by CBS executives. But when it finally aired on December 9, 1965, almost half of all U.S. TV sets were tuned to the broadcast, and the show went on to win an Emmy and a Peabody.
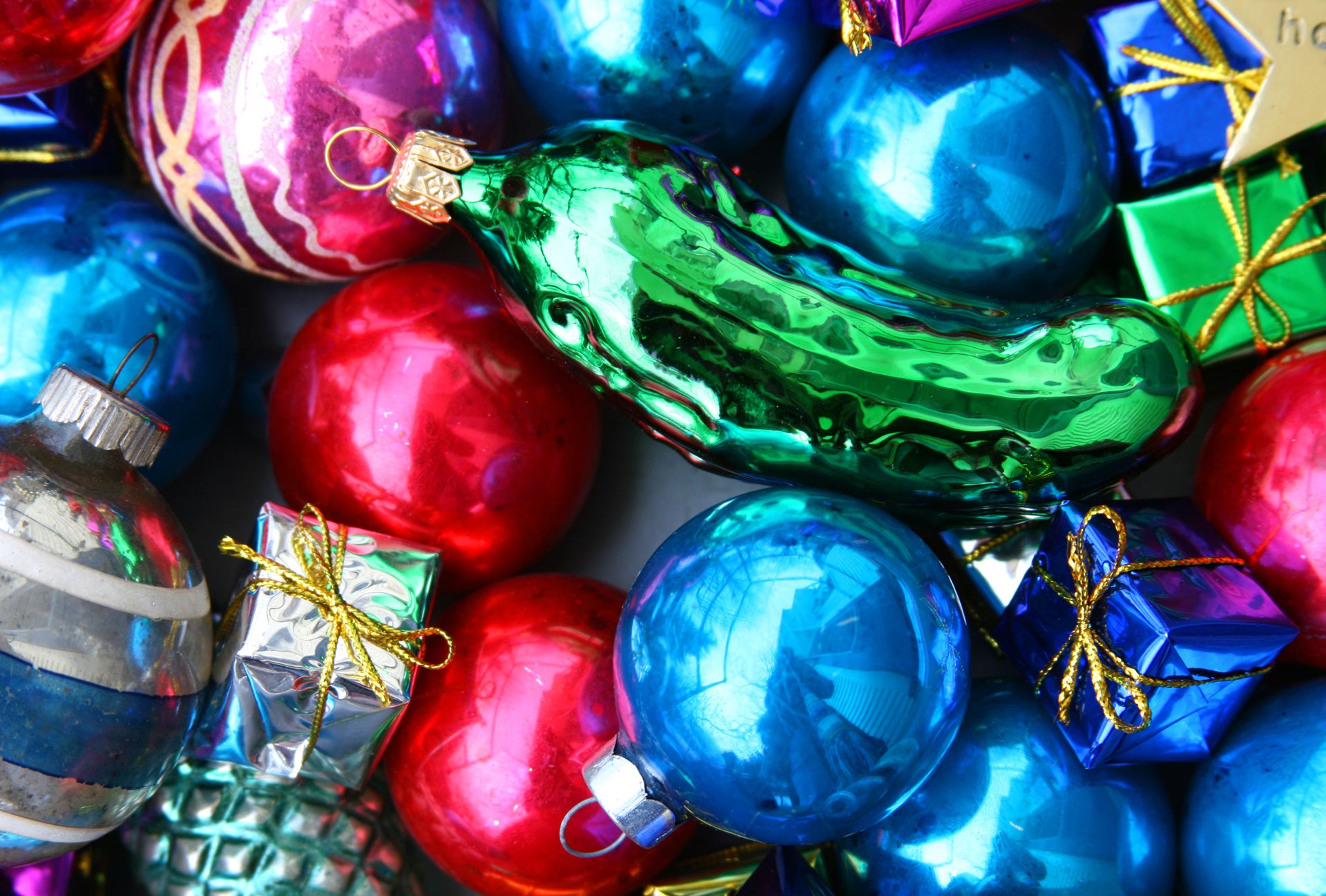

Hiding a green pickle ornament on the tree so that the first child to find it wins a gift, or gets to open the first present is an American tradition. The practice’s origins are a bit murky but it likely it grew from a Woolworths marketing gimmick from the late 1800s.READ MORE: The Origins of 25 Christmas Traditions
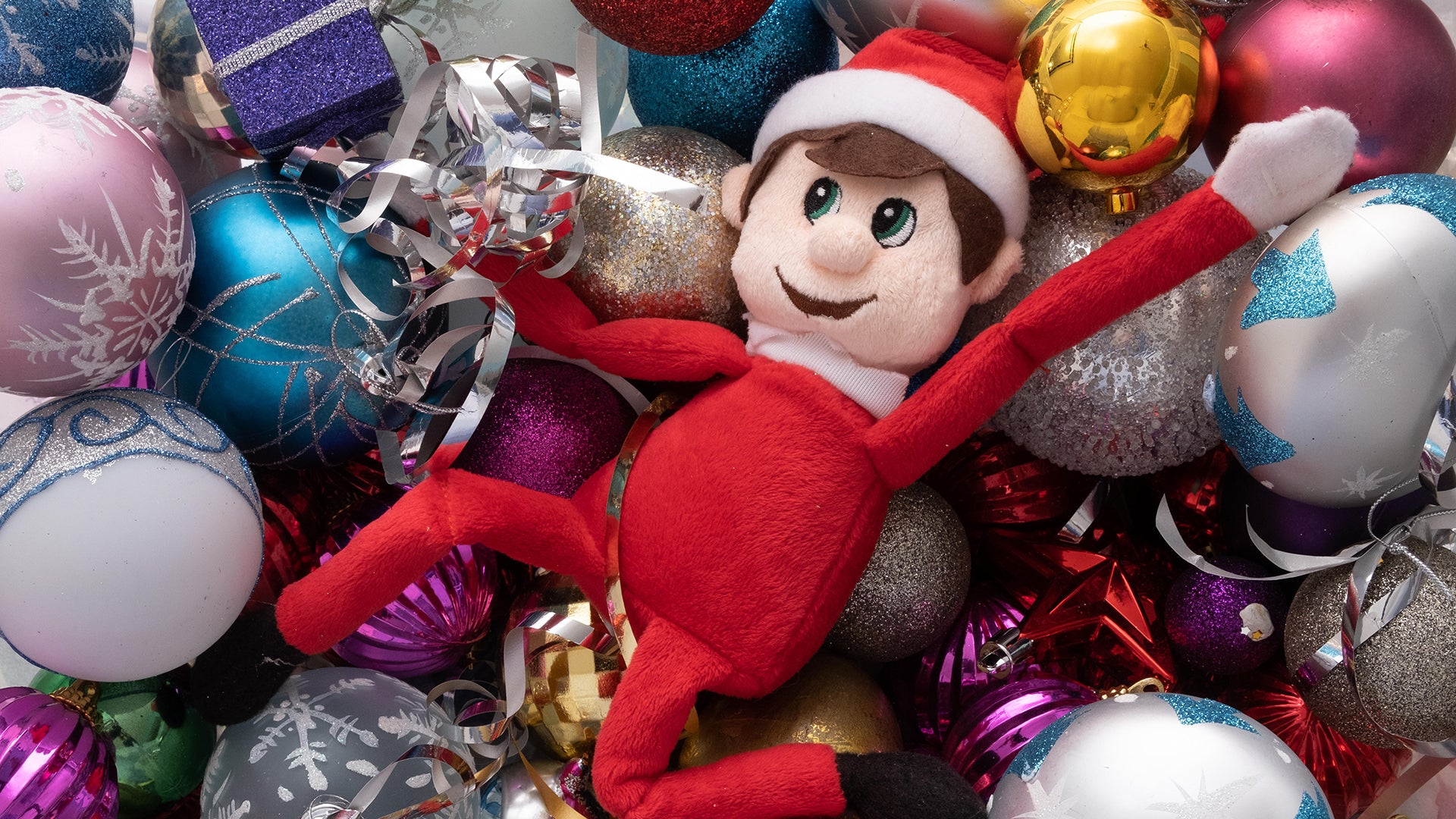

Millions of elves have been “adopted” and hidden each night at Christmas time since 2005 when Carol Aebersold and her daughter, Chanda Bell, published the book Elf on the Shelf: A Christmas Tradition that comes with the toy.
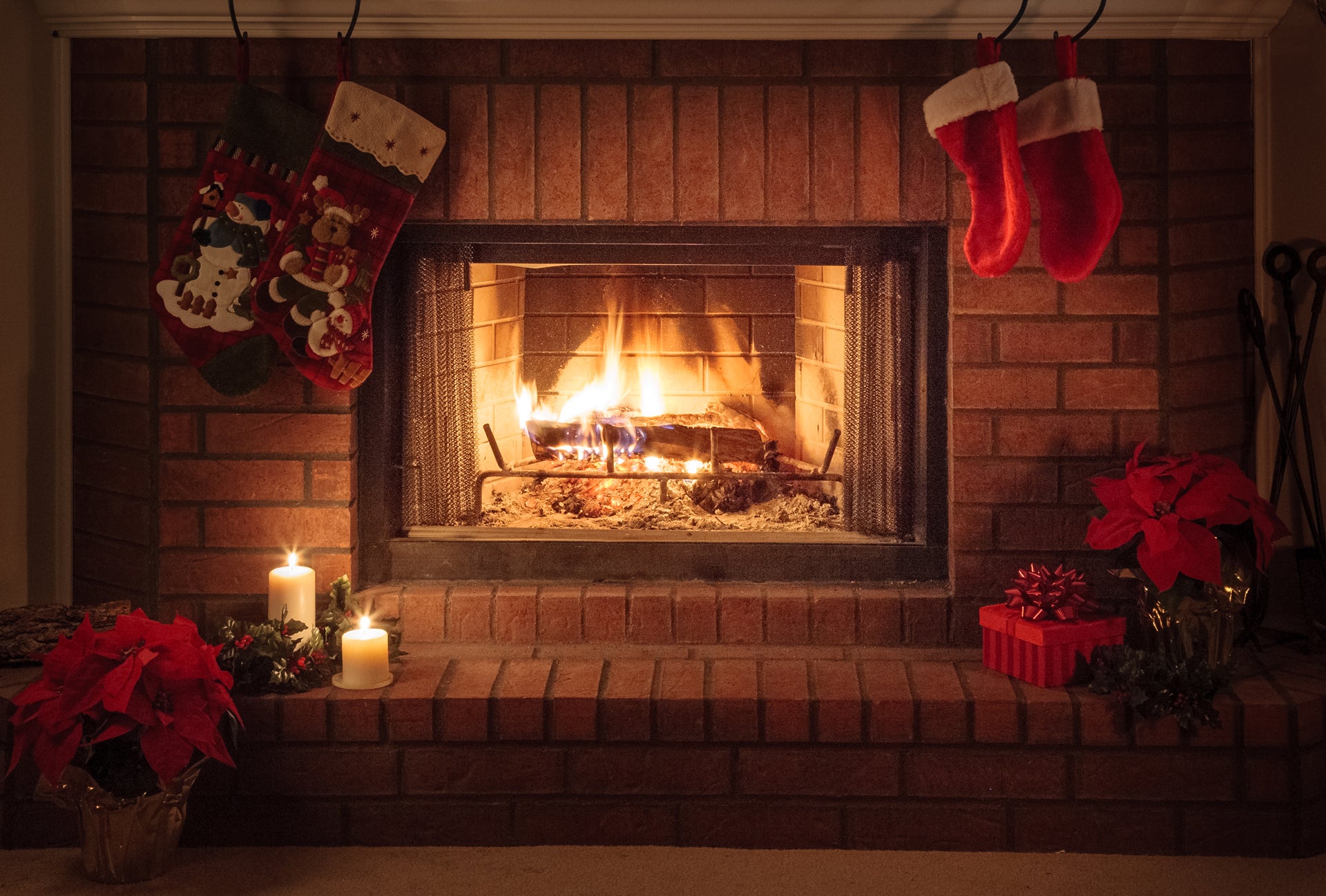

Yule logs were part of ancient winter solstice celebrations, but it was Americans who turned the wood burning into must-see TV. Back in 1966, WPIX-TV in New York City aired a continuous 17-second loop of a fireplace for three hours along with holiday music. Today, you can view the yule log on demand, on YouTube and more.
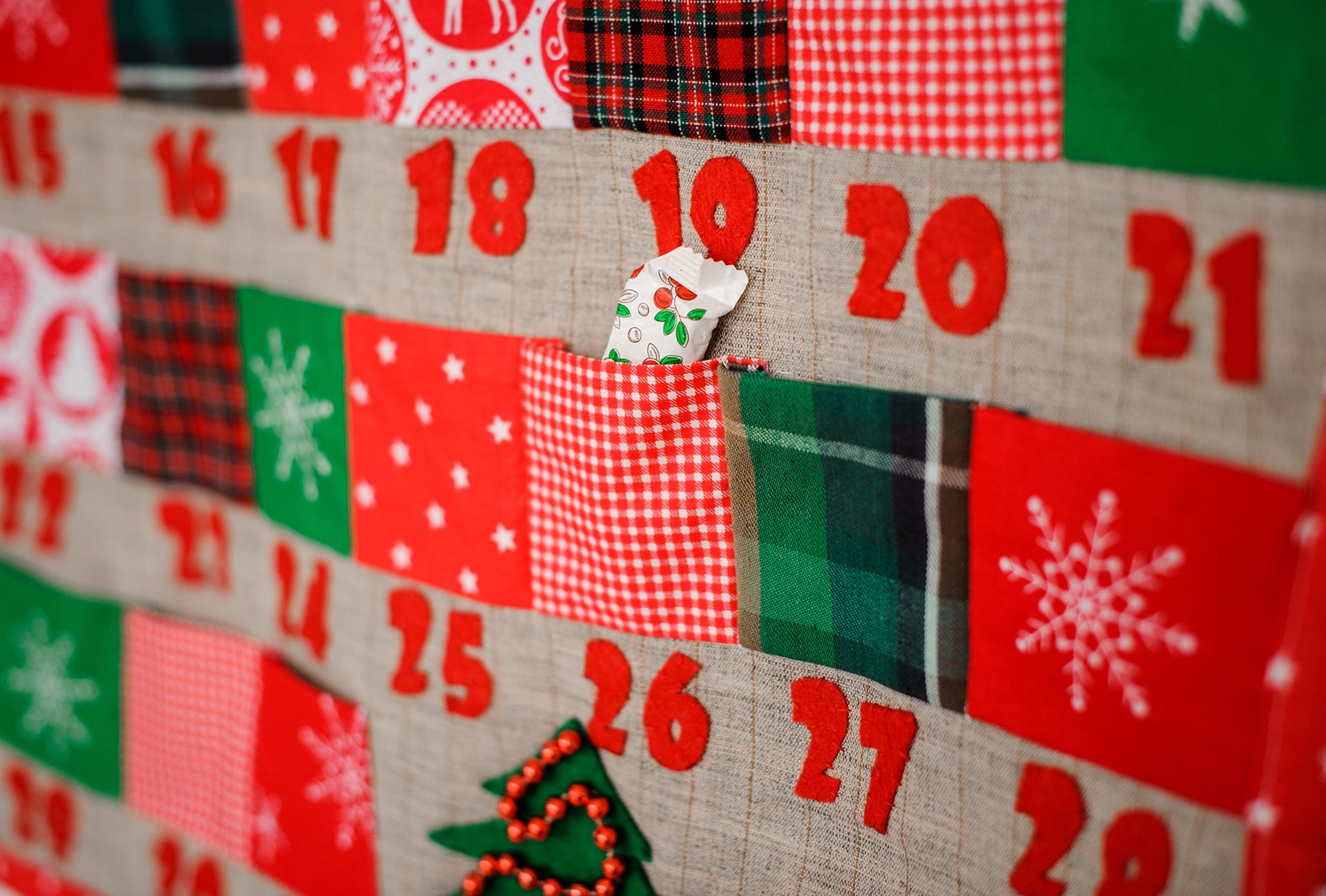

Early versions of this tradition, started in Germany in 1903 by publisher Gerhard Land, offered a way for children to count down to Christmas by opening one “door” or “window” a day to reveal a Bible passage, poem or small gift.
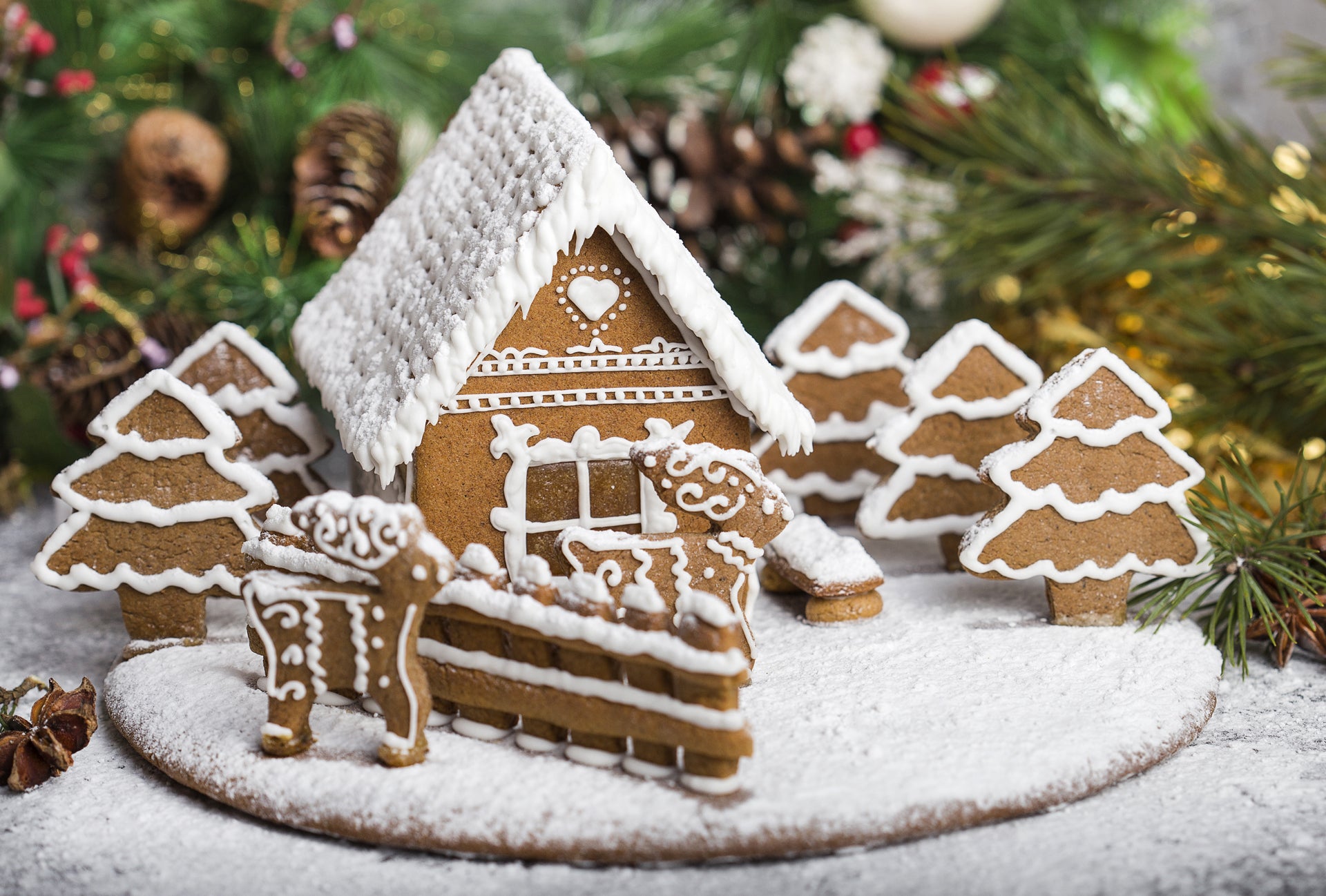

Although Queen Elizabeth I gets credit for the early decorating of gingerbread cookies, Germans lay claim to starting the gingerbread house tradition.
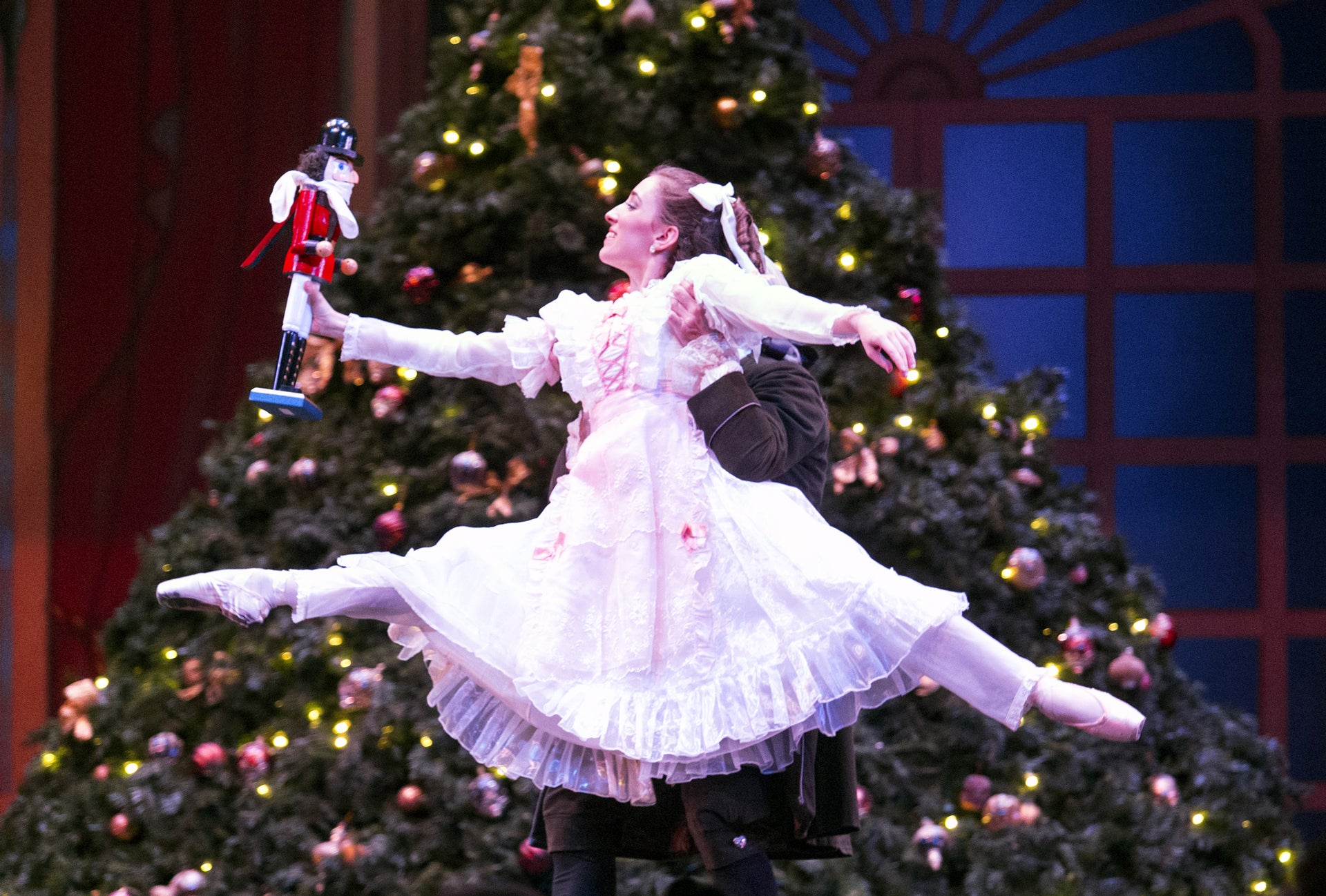

With music by Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky and originally choreographed by Marius Petipa, the romantic tale of the young Clara’s Christmas Eve premiered December 18, 1892, in St. Petersburg, Russia.
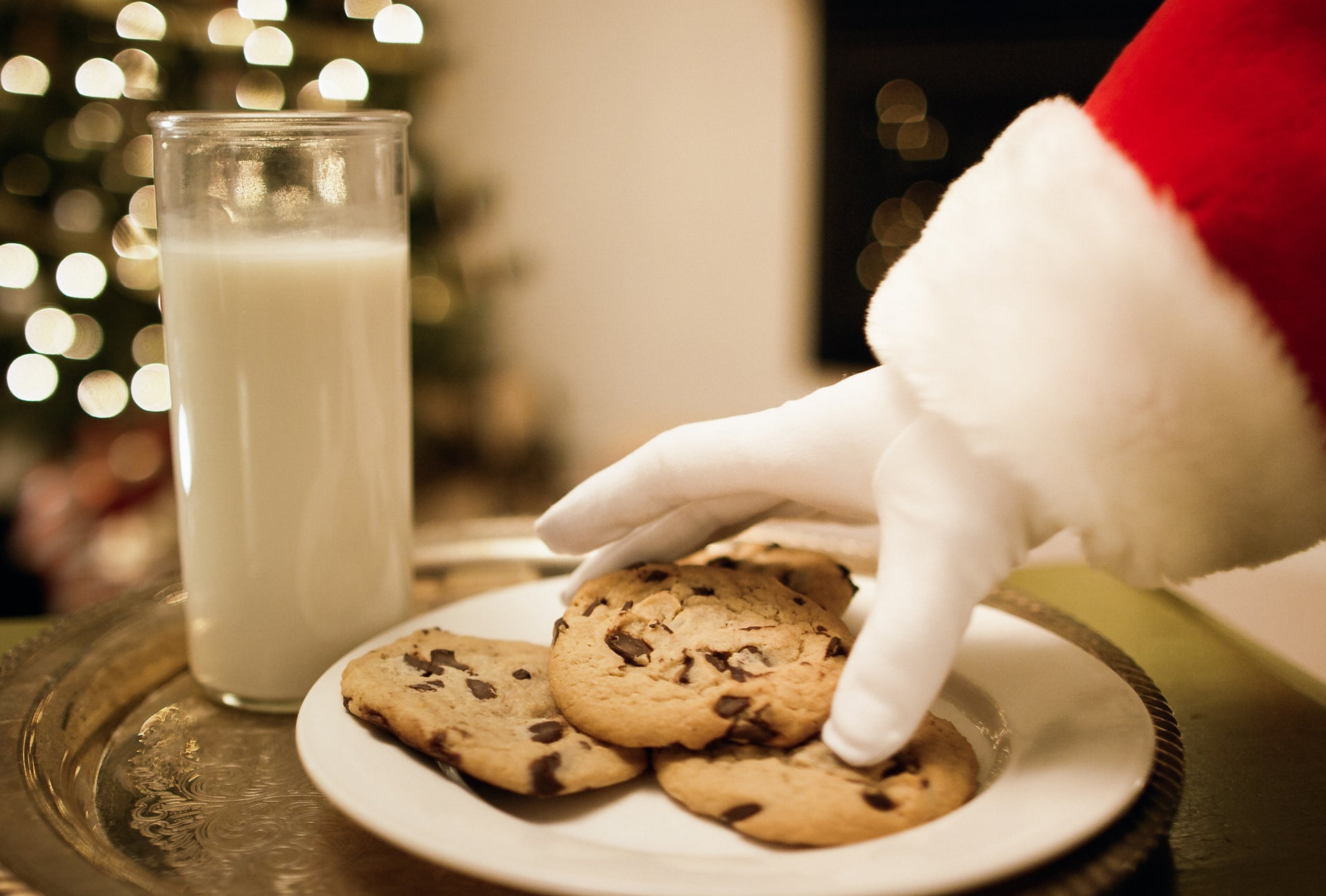

While leaving treats for Santa and his reindeer dates back to ancient Norse mythology, Americans began to sweeten up to the tradition during the Great Depression in the 1930s.
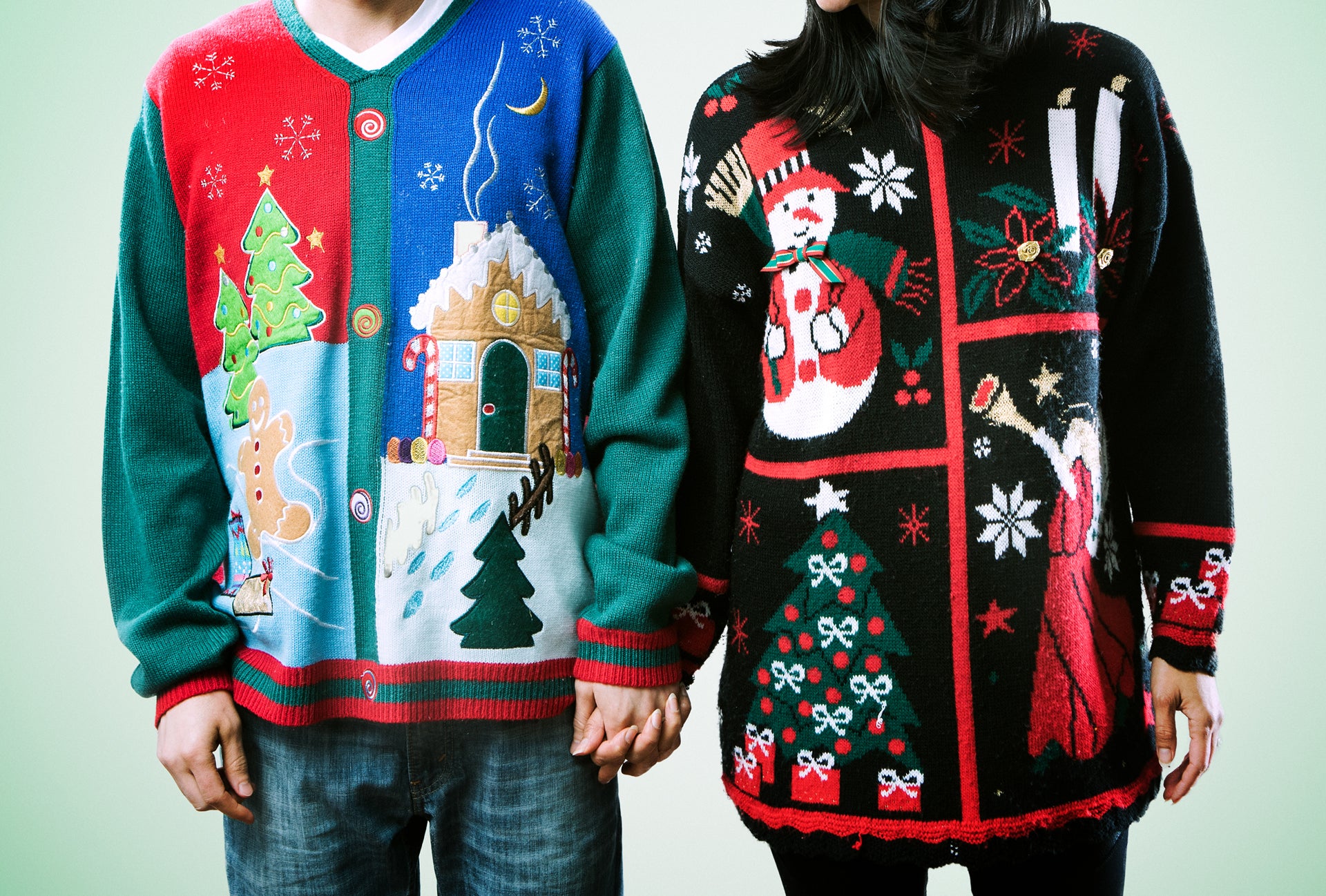

Ugly Christmas sweaters became a party trend in Vancouver, Canada in 2001, according to the Ugly Christmas Sweater Party Book.
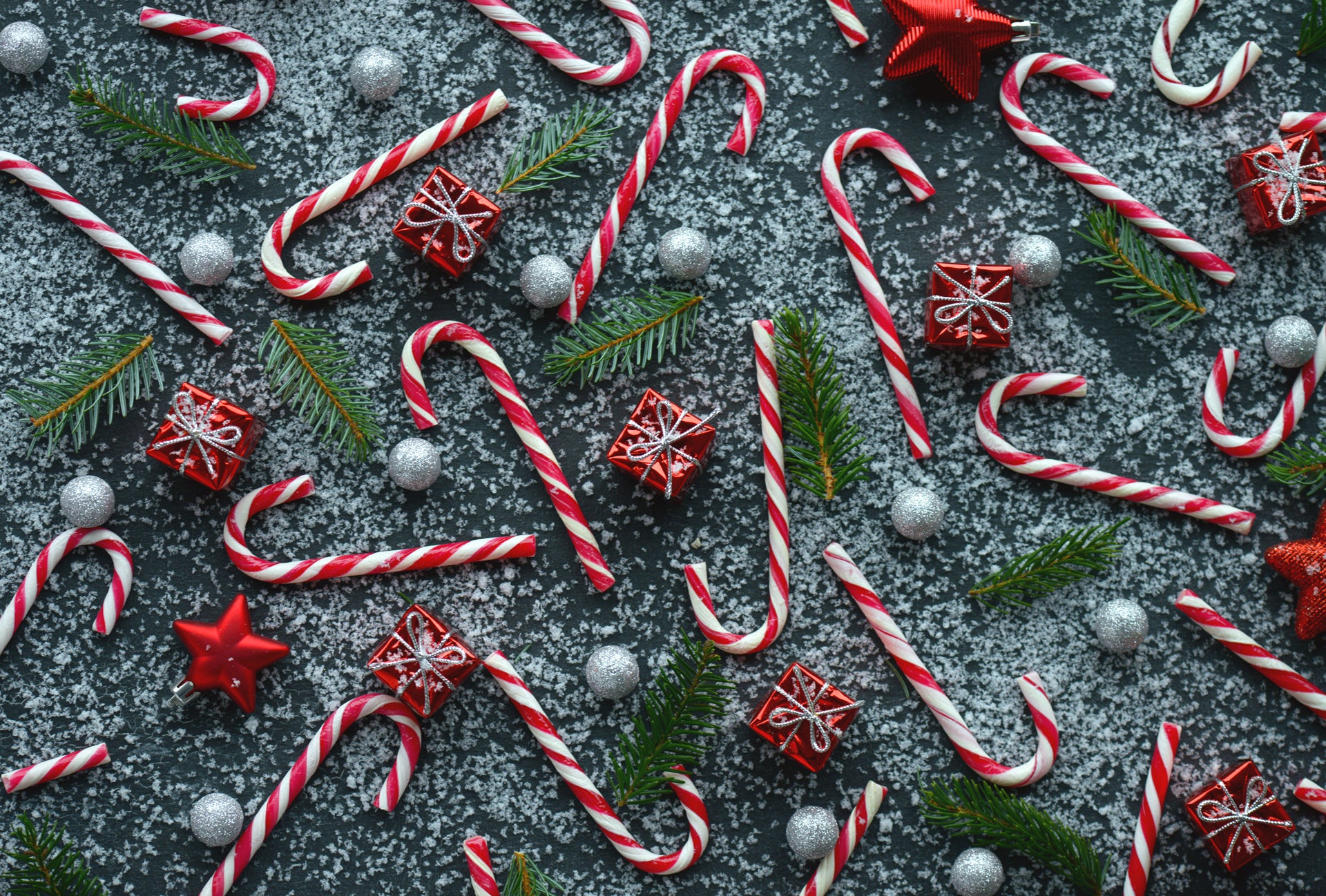

Candy canes date back to 1670 in Germany. The red and white sticks arrived stateside in 1847, when a German-Swedish immigrant in Wooster, Ohio placed them on a tree.
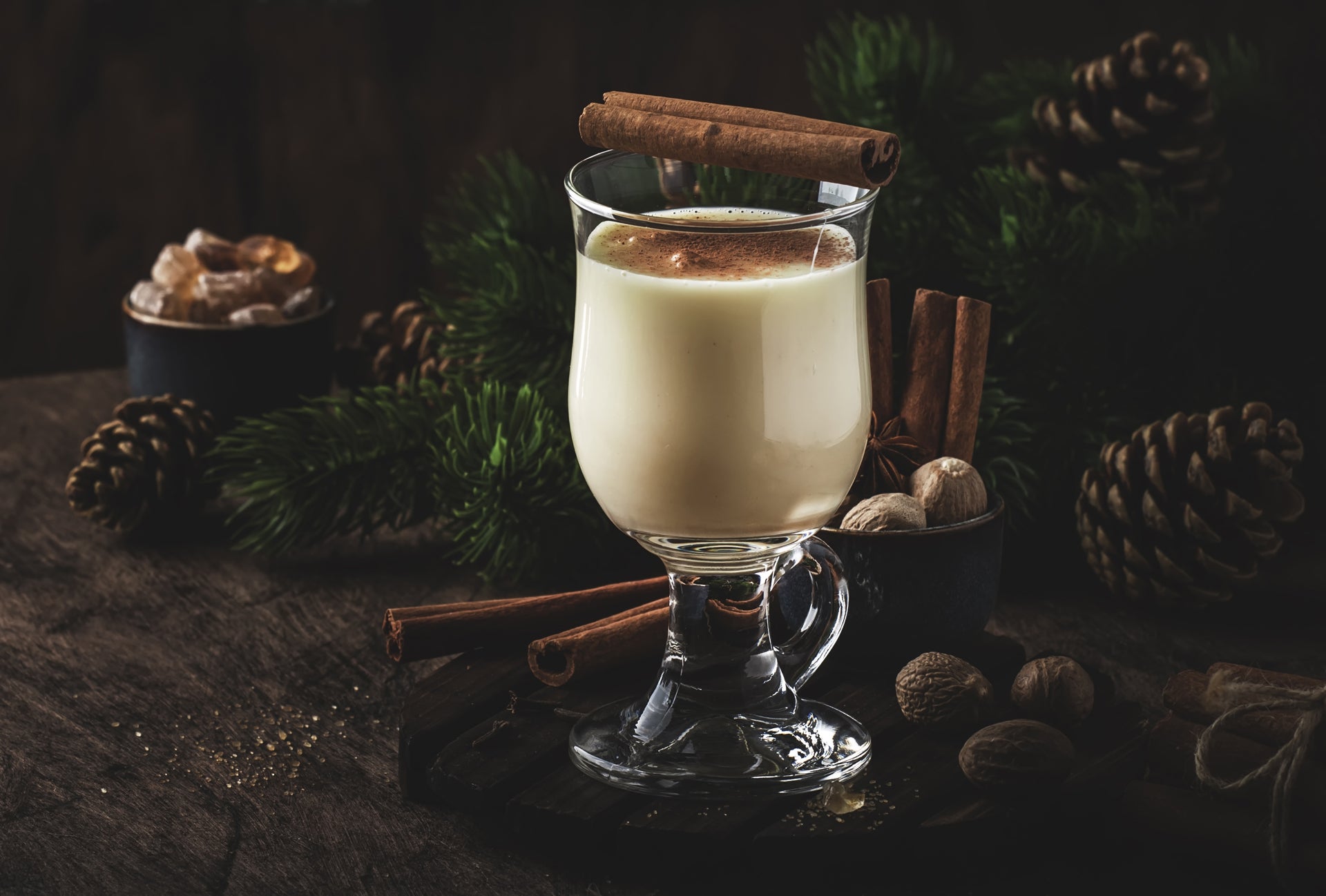

The yuletide cocktail stems from posset, a drink made with hot curdled milk and ale or wine from medieval England. American colonists made it popular by adding rum.
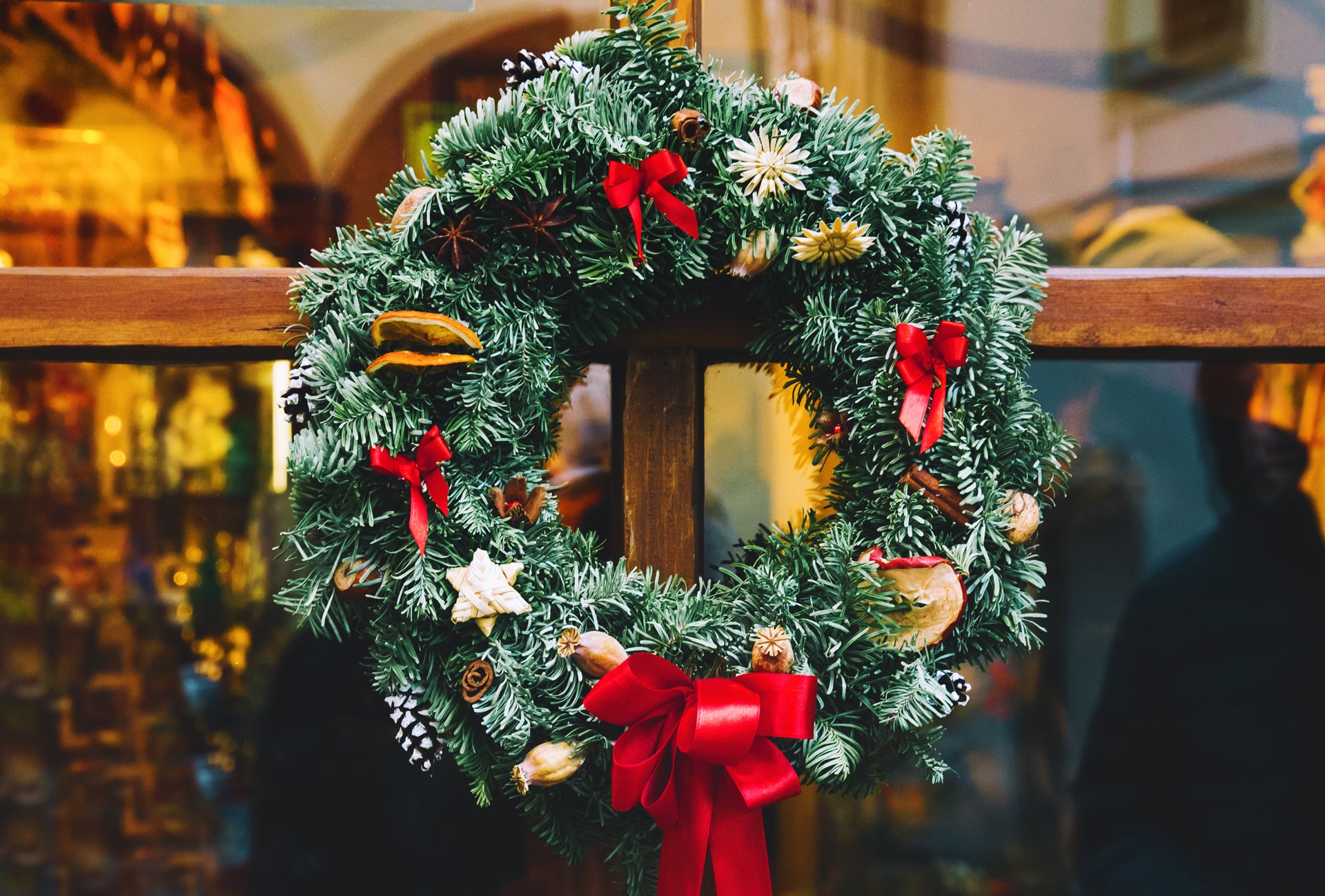

Wreaths have been around since the ancient Greek and Roman times, but they eventually took on Christian meaning, with the circular shape representing eternal life and the holly leaves and berries symbolic of Christ’s crown of thorns and blood.

The first official Christmas card debuted in 1843 England with the message, “A Merry Christmas and a Happy New Year to You.” The idea of a mailed winter holiday greeting gradually caught on in both Britain and the U.S., with the Kansas City-based Hall Brothers (now Hallmark) creating a folded card sold with an envelope in 1915. READ MORE: Some of the Earliest Christmas Cards Were Morbid and Creepy
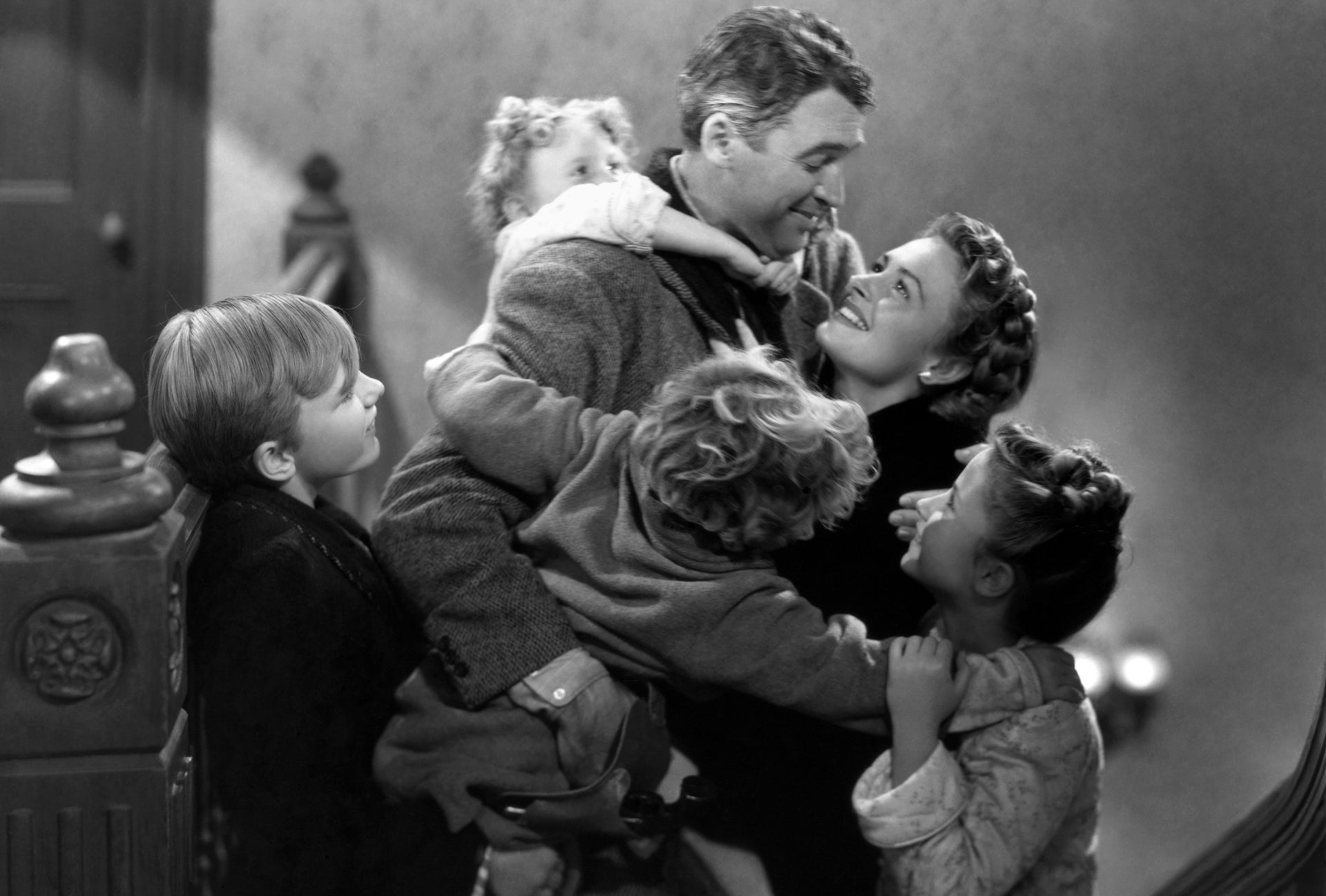

Frank Capra’s classic Christmas film debuted in 1946, with Jimmy Stewart playing George Bailey, a suicidal man who is shown what life would be like without him by an angel. The movie became an annual TV-viewing tradition.

Edward Hibberd Johnson had the bright idea of stringing bulbs around a Christmas tree in New York in 1882.
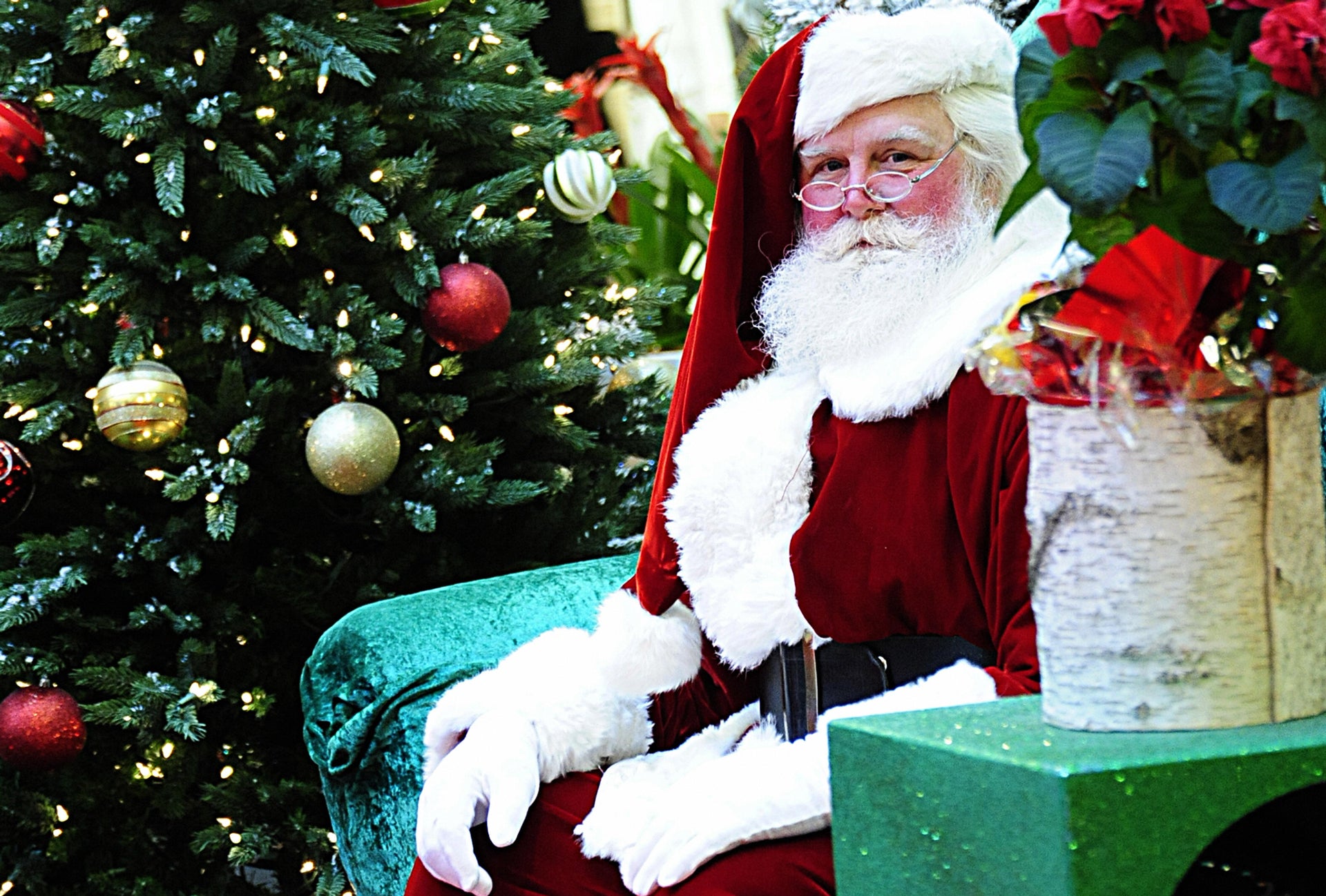

Lining up at the mall to snap a photo of the kids on Santa’s lap may seem like a modern Christmas tradition, but it dates back to 1890, when James Edgar of Brockton, Massachusetts had a Santa suit made for him and dressed as the jolly fellow at his dry goods store.
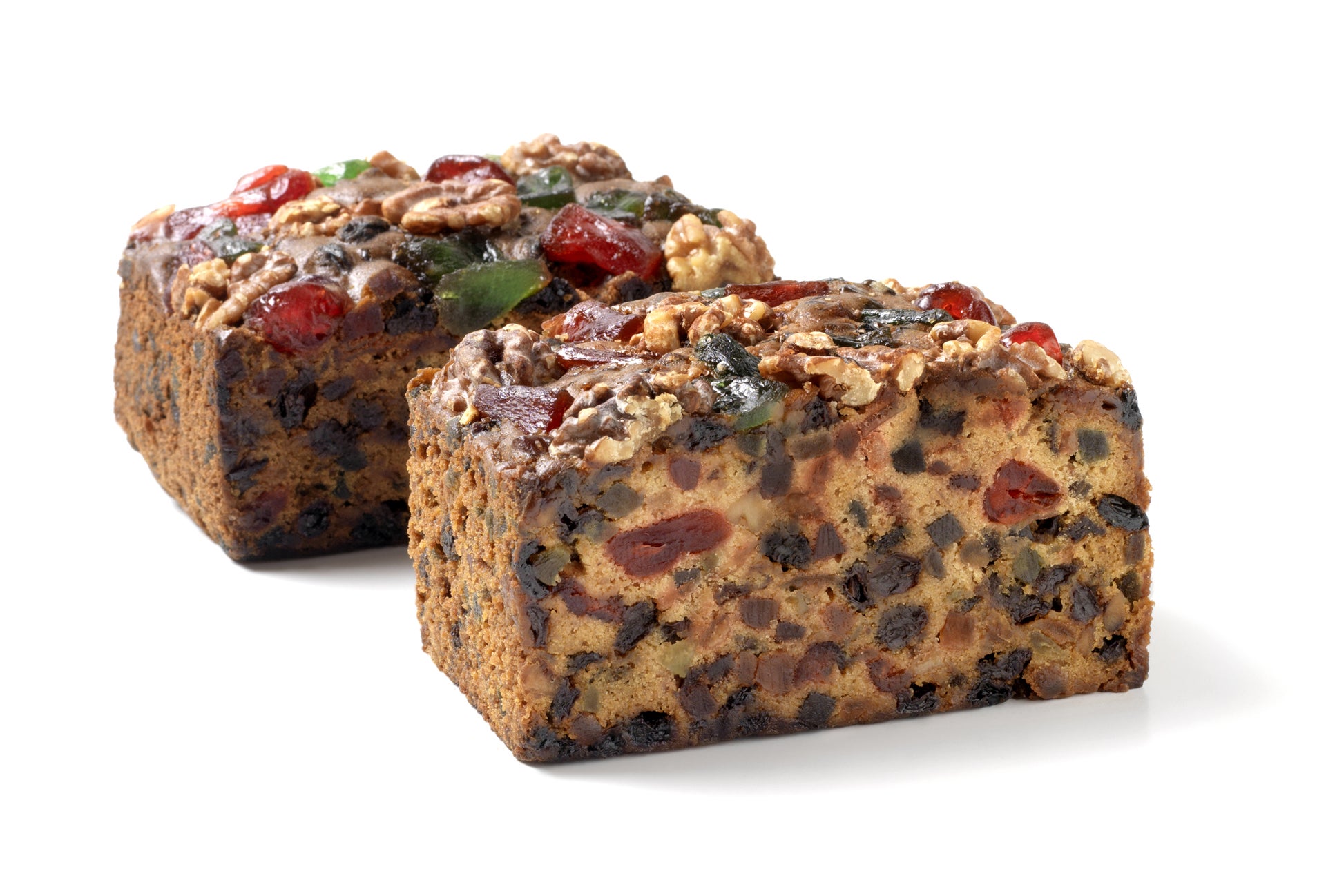

A favorite of the Brits, fruitcake has been the subject of long-running American holiday jokes. Truman Capote wrote a short story about “fruitcake weather” in 1956, the small town of Manitou Springs, Colorado holds an annual Fruitcake Toss Day on January 3.
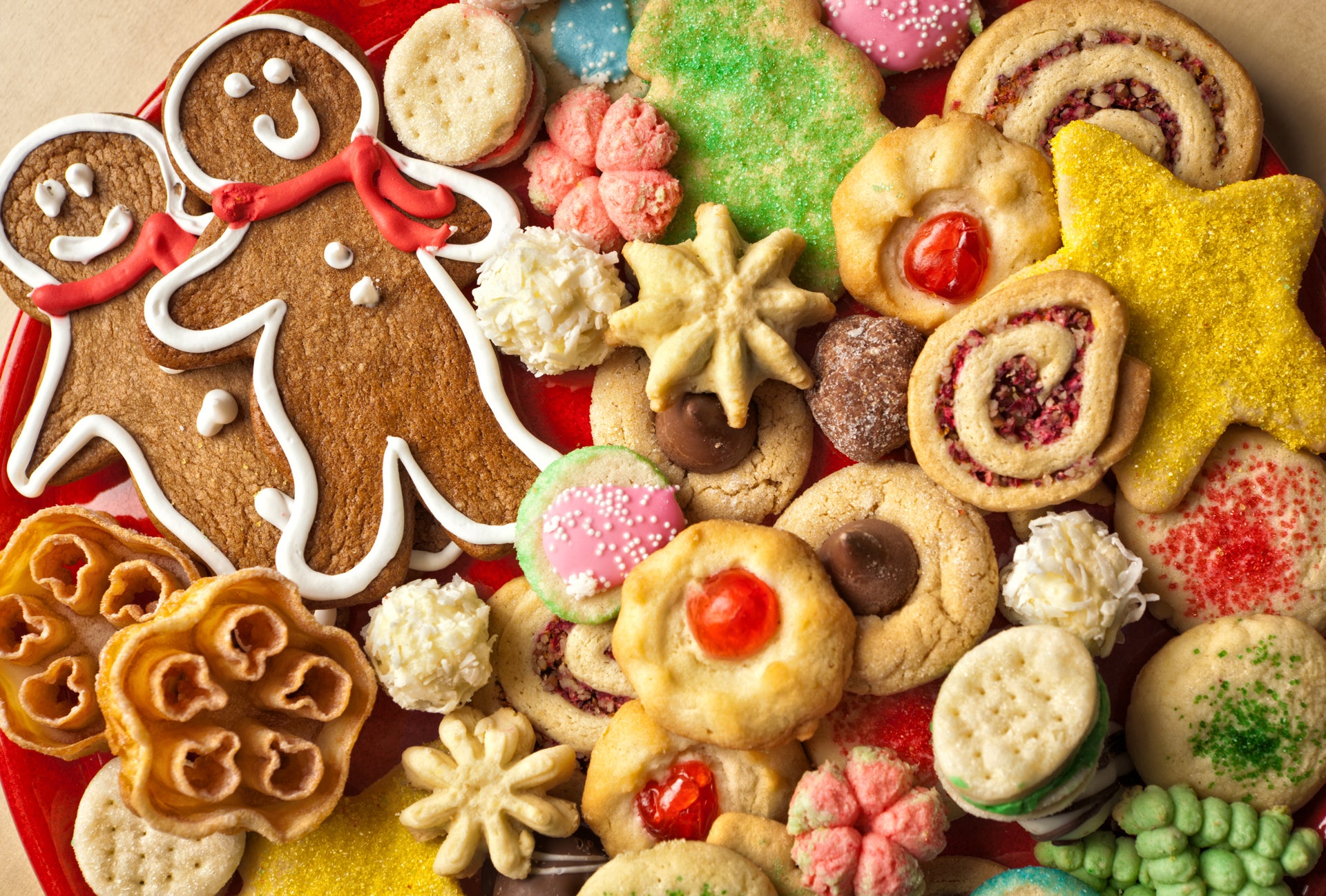

References to “cookie parties” date back to the late 1800s, and they began to be called “cookie exchanges” by the 1930s, and “cookie swaps” in the 1950s.

The reading of this classic by poet Clement Moore is an American holiday tradition. Believed to have been written on Christmas Eve of 1822, the New Yorker is said to have been inspired by his sleigh ride home.
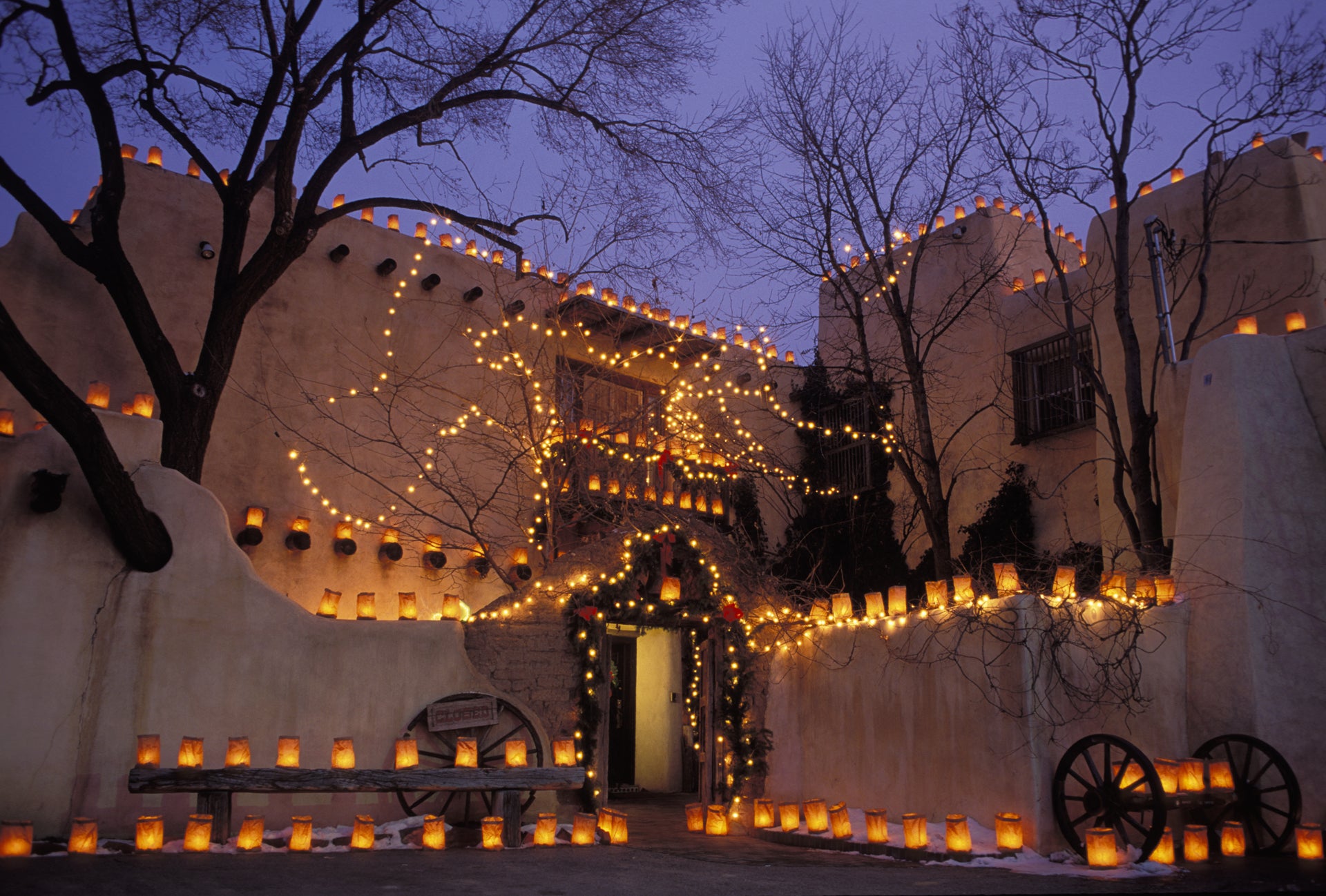

Dating back more than 300 years, luminarias line sidewalks and churches in places such as Albuquerque and Santa Fe, New Mexico.

The Christian 12 days of Christmas, which span the birth of Jesus and the visit of the Magi, actually take place December 25 to January 6. The earliest version of the poem-turned-song is thought to have been published in Mirth With-out Mischief, a children’s book from 1780.
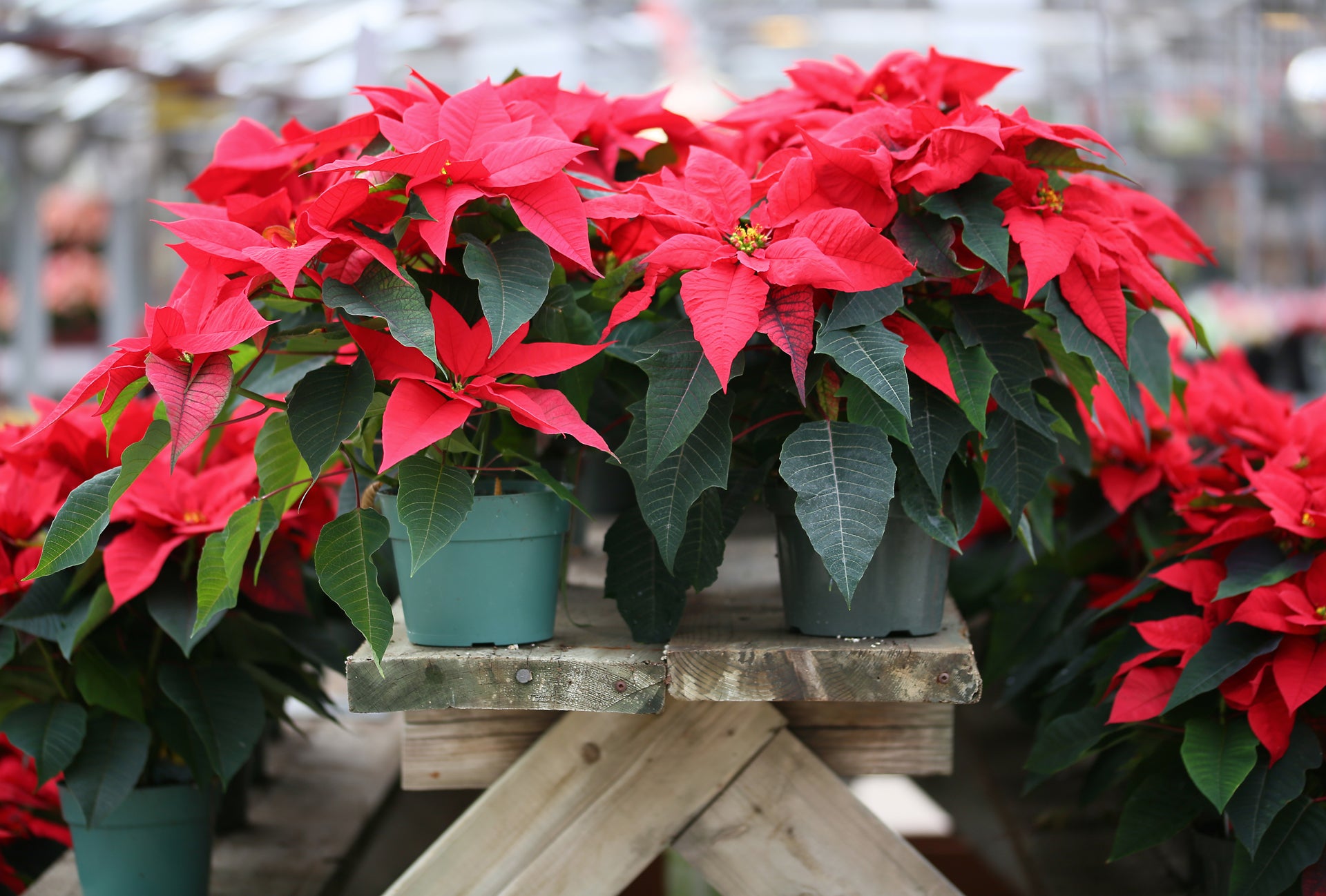

America’s Christmas flower, these plants native to Central America were brought to the United States (and given their name) by the country’s first U.S. ambassador to Mexico, botanist Joel Roberts Poinsett, in the 1820s.

The tradition started in 1891 when San Francisco Salvation Army Capt. Joseph McFee wanted to raise money to offer a free Christmas dinner to 1,000 of the city’s most destitute.
In Rome, where winters were not as harsh as those in the far north, Saturnalia—a holiday in honor of Saturn, the god of agriculture—was celebrated. Beginning in the week leading up to the winter solstice and continuing for a full month, Saturnalia was a hedonistic time, when food and drink were plentiful and the normal Roman social order was turned upside down. For a month, enslaved people were given temporary freedom and treated as equals. Business and schools were closed so that everyone could participate in the holiday's festivities.
Also around the time of the winter solstice, Romans observed Juvenalia, a feast honoring the children of Rome. In addition, members of the upper classes often celebrated the birthday of Mithra, the god of the unconquerable sun, on December 25. It was believed that Mithra, an infant god, was born of a rock. For some Romans, Mithra’s birthday was the most sacred day of the year.
In the early years of Christianity, Easter was the main holiday; the birth of Jesus was not celebrated. In the fourth century, church officials decided to institute the birth of Jesus as a holiday. Unfortunately, the Bible does not mention date for his birth (a fact Puritans later pointed out in order to deny the legitimacy of the celebration). Although some evidence suggests that his birth may have occurred in the spring (why would shepherds be herding in the middle of winter?), Pope Julius I chose December 25. It is commonly believed that the church chose this date in an effort to adopt and absorb the traditions of the pagan Saturnalia festival. First called the Feast of the Nativity, the custom spread to Egypt by 432 and to England by the end of the sixth century.
By holding Christmas at the same time as traditional winter solstice festivals, church leaders increased the chances that Christmas would be popularly embraced, but gave up the ability to dictate how it was celebrated. By the Middle Ages, Christianity had, for the most part, replaced pagan religion.
On Christmas, believers attended church, then celebrated raucously in a drunken, carnival-like atmosphere similar to today’s Mardi Gras. Each year, a beggar or student would be crowned the “lord of misrule” and eager celebrants played the part of his subjects. The poor would go to the houses of the rich and demand their best food and drink. If owners failed to comply, their visitors would most likely terrorize them with mischief. Christmas became the time of year when the upper classes could repay their real or imagined “debt” to society by entertaining less fortunate citizens.
In the early 17th century, a wave of religious reform changed the way Christmas was celebrated in Europe. When Oliver Cromwell and his Puritan forces took over England in 1645, they vowed to rid England of decadence and, as part of their effort, cancelled Christmas. By popular demand, Charles II was restored to the throne and, with him, came the return of the popular holiday.
The pilgrims, English separatists that came to America in 1620, were even more orthodox in their Puritan beliefs than Cromwell. As a result, Christmas was not a holiday in early America. From 1659 to 1681, the celebration of Christmas was actually outlawed in Boston. Anyone exhibiting the Christmas spirit was fined five shillings. By contrast, in the Jamestown settlement, Captain John Smith reported that Christmas was enjoyed by all and passed without incident.
After the American Revolution, English customs fell out of favor, including Christmas. In fact, Christmas wasn’t declared a federal holiday until June 26, 1870.
It wasn’t until the 19th century that Americans began to embrace Christmas. Americans re-invented Christmas, and changed it from a raucous carnival holiday into a family-centered day of peace and nostalgia. But what about the 1800s piqued American interest in the holiday?
The early 19th century was a period of class conflict and turmoil. During this time, unemployment was high and gang rioting by the disenchanted classes often occurred during the Christmas season. In 1828, the New York city council instituted the city’s first police force in response to a Christmas riot. This catalyzed certain members of the upper classes to begin to change the way Christmas was celebrated in America.
In 1819, best-selling author Washington Irving wrote The Sketchbook of Geoffrey Crayon, gent., a series of stories about the celebration of Christmas in an English manor house. The sketches feature a squire who invited the peasants into his home for the holiday. In contrast to the problems faced in American society, the two groups mingled effortlessly. In Irving’s mind, Christmas should be a peaceful, warm-hearted holiday bringing groups together across lines of wealth or social status. Irving’s fictitious celebrants enjoyed “ancient customs,” including the crowning of a Lord of Misrule. Irving’s book, however, was not based on any holiday celebration he had attended—in fact, many historians say that Irving’s account actually “invented” tradition by implying that it described the true customs of the season.
Also around this time, English author Charles Dickens created the classic holiday tale, A Christmas Carol. The story’s message-the importance of charity and good will towards all humankind-struck a powerful chord in the United States and England and showed members of Victorian society the benefits of celebrating the holiday.
The family was also becoming less disciplined and more sensitive to the emotional needs of children during the early 1800s. Christmas provided families with a day when they could lavish attention-and gifts-on their children without appearing to “spoil” them.
As Americans began to embrace Christmas as a perfect family holiday, old customs were unearthed. People looked toward recent immigrants and Catholic and Episcopalian churches to see how the day should be celebrated. In the next 100 years, Americans built a Christmas tradition all their own that included pieces of many other customs, including decorating trees, sending holiday cards and gift-giving.
Although most families quickly bought into the idea that they were celebrating Christmas how it had been done for centuries, Americans had really re-invented a holiday to fill the cultural needs of a growing nation.
The legend of Santa Claus can be traced back to a monk named St. Nicholas who was born in Turkey around A. D. 280. St. Nicholas gave away all of his inherited wealth and traveled the countryside helping the poor and sick, becoming known as the protector of children and sailors.
St. Nicholas first entered American popular culture in the late 18th century in New York, when Dutch families gathered to honor the anniversary of the death of “Sint Nikolaas” (Dutch for Saint Nicholas), or “Sinter Klaas” for short. “Santa Claus” draws his name from this abbreviation.
In 1822, Episcopal minister Clement Clarke Moore wrote a Christmas poem called “An Account of a Visit from St. Nicholas,” more popularly known today by it’s first line: “‘Twas The Night Before Christmas.” The poem depicted Santa Claus as a jolly man who flies from home to home on a sled driven by reindeer to deliver toys.
The iconic version of Santa Claus as a jolly man in red with a white beard and a sack of toys was immortalized in 1881, when political cartoonist Thomas Nast drew on Moore's poem to create the image of Old Saint Nick we know today.

Nicholas – The man who loved to help in secret
The man behind today’s figure of Father Christmas or Santa Claus was born in the 3rd century modern-day Turkey. Nicholas was born in a wealthy family and in his early years he was brought up by his parents to be a devout Christian. Sadly his parents died when he was only a teenager. Subsequently, he went to live with his uncle who was a priest. Responding to Christ’s radical call to “give everything and come follow me”, he gave away his inherited wealth. Because of his zeal in adhering to his faith, he spent a number of years in prison under the Roman Emperor Diocletian who ruthlessly persecuted Christians. After his release from prison, he became renowned for his generosity to those in need, his love for children, his concern for those who suffer injustice, as well as for his care for sailors.
Nicholas, the real Santa Claus, tried to give his help secretly. He didn’t want any attention or to be thanked. A number of years after his imprisonment had passed and he was appointed to become the Bishop of Myra. His concern for his flock went beyond religious regard. When Myra was affected by famine he negotiated with some sailors who were coming from Egypt, and bought wheat for the people so that no one went hungry. He helped many, young and old, who were in trouble. All his life Nicholas showed people how to love God and care for others.
The custom of giving presents in a stocking at Christmas time originates from Nicholas
In St Nicholas’ days, there was a rich man, who had fallen on hard times. Since the man could not afford a dowry for his three daughters, they were bound to a life of slavery or prostitution as they would remain unmarried, and unable to earn a living in any other way. It is said that St Nicholas heard of the family’s plight, and secretly delivered gold to the family right before each daughter came of age. St Nicholas, the real Santa Claus wanted to keep his charity a secret. So each time he dropped a sack full of gold down the chimney, it landed in the girl’s stocking, which was hanging on the fireplace mantel to dry.
The Real Santa ClausFrom St Nicholas to Santa Claus
After Nicholas died, the people told stories of the good and kind things Nicholas had done. Sailors spread these stories about St Nicholas wherever they went. There were stories about his special care he had for children, saving the innocent from injustice, providing food during time of famine and calming the seas. As people heard about the good and kind St Nicholas, they wanted to imitate him. Since the liturgical feast of St Nicholas falls during the Advent period, for these past 1000 years St Nicholas has become associated with Christmas. In recent centuries, the custom of children receiving gifts on the eve of St Nicholas’ day originated, particularly in Northern European countries. The devotion towards St Nicholas was so strong that the tradition to this day, in a number of European countries with a predominant Protestant tradition.
1822 – Saint Nicholas in Poetry
An early and famous poem, called, A Visit From St Nicholas was written by Dr. Clement Clarck Moore for his own six children. This poem is also known by its first line ”Twas the Night Before Christmas”.
‘Twas the night before Christmas, when all through the house Not a creature was stirring, not even a mouse; The stockings were hung by the chimney with care, In hopes that St Nicholas soon would be there; …
Christmas stocking meaning1864 – Saint Nicholas in Song In 1864, Benjamin Hanby wrote the song “Up on the House Top” which was probably inspired by Dr. Clement Clarck Moore poem.
“Up on the house top, click, click, click, Down through the chimney with good Saint Nicholas…
1920’s – Saint Nicholas in Advertising
Since the 1920’s Santa Claus was depicted in cartoon art in a bright red suit. He became entrenched in the social imagination as a jovial character after his image was used by a beverage company to endorse its drink as being the solution for ‘a thirst for all seasons’. Other businesses’ were quick to follow, using the jovial Santa Claus to advance the commercial emphasis that dominates Christmas today.
Father Christmas and Saint Nicholas playmobil
However, symbols of the real Santa were also used such as the crimson or deep purple characteristics colours of bishop’s robes, the bishop’s crozier (a shepherd’s hooked staff), the mitre (a bishop’s pointy hat), and a book symbolising the Sacred Scriptures. Other symbols related to the stories about him include, a ship or anchor, hanging the stockings by the fireplace and candy canes.
Buying children's gifts thoughtfullySuggestion for gifts for children
It is recommended that parents or helpers of St Nicholas buy small presents for children and help them appreciate these gifts rather than buying big presents or having the children ask for a particular present which they would like.
Thank you to Professor Adrian Gellel for the historical details in this article.
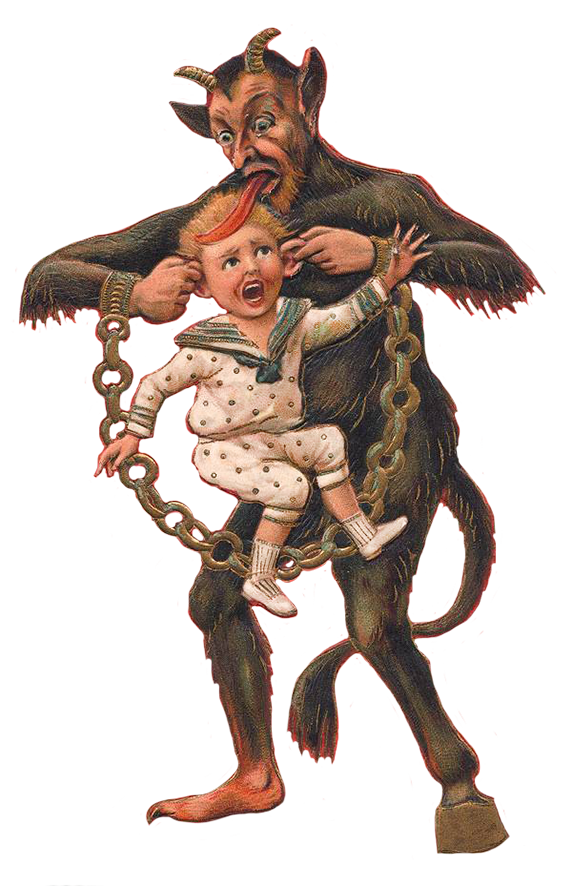

Oh, wait! There is something else in those boots! A bundle of golden twigs? Just before St Nicholas feast day, there will be street vendors of golden twigs in all the Croatian cities. You will even be able to get them in a local store. What’s with that?
The answer will unlock the secret of that concerned look in the children’s eyes. That’s because… St Nicholas never travels alone. There is a monster that he drags along in chains. It’s Krampus! Krampus is a devilish creature all covered in hair, with horns, and a tongue that goes all the way to the ground. He carries a giant sack and takes the naughty children with him! He’s the one who leaves the twigs as a warning.
In some countries, like Germany, Austria, and even our neighbor Slovenia, the tradition of Krampus is still very much alive. Here in Zagreb, not that much. Only some families still introduce Krampus into their daily lives a few days before he arrives. Those are a few days of heaven on earth for the adults: children are so obedient, their rooms clean, and all you did was casually mention Krampus.
However, this is nothing compared to the past times. Back in the day, they really did their best to scare the kids on that day. Every neighborhood in Zagreb had its own pair, a St Nicholas dressed as a bishop, and a Krampus. They visited each and every house. If you lived at one end of a street, you could hear them coming when they were still at the other end. Krampus yelled: “Where are the naughty children? I want to put them in my bag!” with that terrifying sound of chains.
Then they came to your house. St Nicholas took his time, slowly trying to find your name in his book of good children. Very slowly. He couldn’t find it at first. All that time, Krampus is shouting: “They’re not in your book, they‘re the naughty ones, give them to me!”
The poor children are on their knees, saying every single prayer they know or don’t know, changing colors, sweating! Finally, St Nicholas finds their name after all. Phew!
They receive a few walnuts as a reward for being good kids all year long. Now, try to imagine what a grateful child looks like. The handful of walnuts was the best gift ever!!
Some things have changed. One thing hasn’t. St Nicholas feast day, December the 6th is when we truly feel Christmas entering our homes in Croatia. Once Krampus is gone and the present is here, you know you’ve been a good child, and you have a whole careless year in front of you! Joy and relief together! Oh, don’t we love our children when we offer them this beautiful combination of feelings!
Traditions have changed. Don’t worry! We don’t torture children anymore like that. If the big presents aren’t enough, we sometimes even tell them that the golden branches are in their boots because they were good. They wouldn’t be golden if they were left by Krampus as a threat, right?
The truth is, in the past, they weren’t golden, and they were meant as a menace that you would get spanked by birch twigs left by Krampus himself!!! Reminder, reminder, be good, be good!
These days, ehm… parents who can’t resist that little sadistic connection with their roots… and think that it’s hilarious to take some chains and make them rattle in the middle of St Nicholas eve… Parents like that are considered messed up.
Citation Information
Article TitleHistory of Christmas
AuthorHistory.com Editors
Website NameHISTORY
URL https://www.history.com/topics/christmas/history-of-christmas
Date AccessedDecember 18, 2023
PublisherA&E Television Networks
Last UpdatedDecember 21, 2022
Original Published DateOctober 27, 2009